Curve Guide¶
Curve Guide force field.
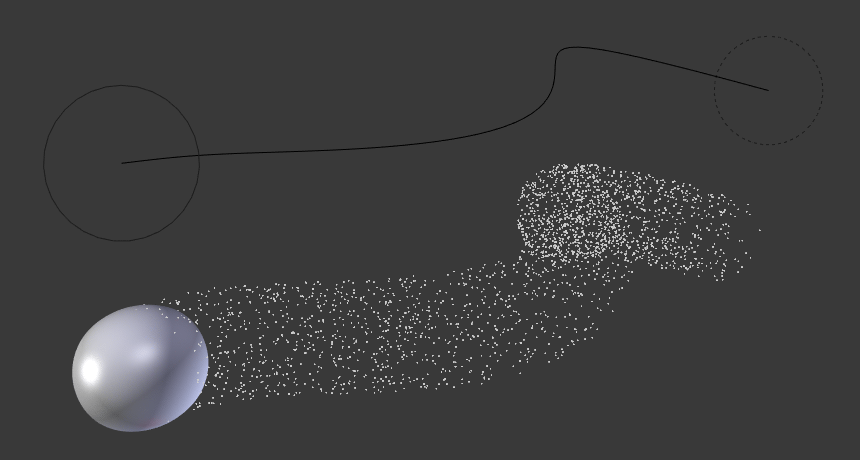
The Curve Guide is used to force particles to follow a certain path defined by a Curve Object. A typical scenario would be to move a red blood cell inside a vein, or to animate the particle flow in a motor. You can also use Curve Guide to shape certain hair strands.
Note
You can also use the Particle Edit Mode to define a path.
Since you can animate curves as Softbody or any other usual way, you may build very complex animations while keeping great control and keeping the simulation time to a minimum.
The option Curve Follow does not work for particles. Instead you have to set Angular Velocity (Particle system tab) to Spin and leave the rotation constant (i.e. do not turn on Dynamic).
Curve Guide s affect all particles on the same layer, independently from their distance to the curve. If you have several guides in a layer, their fields add up to each other (the way you may have learned it in your physics course). But you can limit their influence radius by changing there Minimum Distance (see below).
Note
The Curve Guide does not affect Softbodies.
Options¶
- Minimum Distance
- The distance from the curve, up to where the force field is effective with full strength. If you have a Fall-off of 0 this parameter does nothing, because the field is effective with full strength up to Max Distance (or the infinity). Min Distance is shown with a circle at the endpoints of the curve in the 3D View.
- Free
- Fraction of particle life time, that is not used for the curve.
- Fall-off
- This setting governs the strength of the guide between Min Distance and Max Distance. A Fall-off of 1 means a linear progression.
Path¶
A particle follows a Curve Guide during its lifetime, the velocity depends on its lifetime and the length of the path.
- Additive
- If you use Additive, the speed of the particles is also evaluated depending on the Fall-off.
- Weights
- Use Curve weights to influence the particle influence along the curve.
- Maximum Distance / Use Max
- The maximum influence radius. Shown by an additional circle around the curve object.
Clumping¶
The other settings govern the form of the force field along the curve.
- Clumping Amount
- The particles come together at the end of the curve (1) or they drift apart (-1).
- Shape
- Defines the form in which the particles come together. +0.99: the particles meet at the end of the curve. 0: linear progression along the curve. -0.99: the particles meet at the beginning of the curve.
Kink¶
Changes the shape that the particles can take:
- Type
- Curl
- The radius of the influence depends on the distance of the curve to the emitter.
- Radial
- A three dimensional, standing wave.
- Wave
- A two dimensional, standing wave.
- Braid
- Braid.
- Roll
- An one dimensional, standing wave.
It is not so easy to describe the resulting shapes, so have a look at the example below.

Kink options of a curve guide. From left to right: Radial, Wave, Braid, Roll. Animation.
- Axis
- ToDo.
- Frequency
- The frequency of the offset.
- Amplitude
- The Amplitude of the offset.
- Shape
- Adjust the offset to the beginning/end.